Whole document tree
|
JavaTM 2 Platform Std. Ed. v1.3.1 |
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: INNER | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||
java.awt
Class GridBagLayout
java.lang.Object | +--java.awt.GridBagLayout
- All Implemented Interfaces:
- LayoutManager, LayoutManager2, Serializable
- public class GridBagLayout
- extends Object
- implements LayoutManager2, Serializable
- extends Object
The GridBagLayout class is a flexible layout
manager that aligns components vertically and horizontally,
without requiring that the components be of the same size.
Each GridBagLayout object maintains a dynamic
rectangular grid of cells, with each component occupying
one or more cells, called its display area.
Each component managed by a grid bag layout is associated
with an instance of
GridBagConstraints
that specifies how the component is laid out within its display area.
How a GridBagLayout object places a set of components
depends on the GridBagConstraints object associated
with each component, and on the minimum size
and the preferred size of the components' containers.
To use a grid bag layout effectively, you must customize one or more
of the GridBagConstraints objects that are associated
with its components. You customize a GridBagConstraints
object by setting one or more of its instance variables:
GridBagConstraints.gridx,GridBagConstraints.gridy- Specifies the cell at the upper left of the component's display area,
where the upper-left-most cell has address
gridx = 0,gridy = 0. UseGridBagConstraints.RELATIVE(the default value) to specify that the component be just placed just to the right of (forgridx) or just below (forgridy) the component that was added to the container just before this component was added. GridBagConstraints.gridwidth,GridBagConstraints.gridheight- Specifies the number of cells in a row (for
gridwidth) or column (forgridheight) in the component's display area. The default value is 1. UseGridBagConstraints.REMAINDERto specify that the component be the last one in its row (forgridwidth) or column (forgridheight). UseGridBagConstraints.RELATIVEto specify that the component be the next to last one in its row (forgridwidth) or column (forgridheight). GridBagConstraints.fill- Used when the component's display area
is larger than the component's requested size
to determine whether (and how) to resize the component.
Possible values are
GridBagConstraints.NONE(the default),GridBagConstraints.HORIZONTAL(make the component wide enough to fill its display area horizontally, but don't change its height),GridBagConstraints.VERTICAL(make the component tall enough to fill its display area vertically, but don't change its width), andGridBagConstraints.BOTH(make the component fill its display area entirely). GridBagConstraints.ipadx,GridBagConstraints.ipady- Specifies the component's internal padding within the layout,
how much to add to the minimum size of the component.
The width of the component will be at least its minimum width
plus
(ipadx * 2)pixels (since the padding applies to both sides of the component). Similarly, the height of the component will be at least the minimum height plus(ipady * 2)pixels. GridBagConstraints.insets- Specifies the component's external padding, the minimum amount of space between the component and the edges of its display area.
GridBagConstraints.anchor- Used when the component is smaller than its display area
to determine where (within the display area) to place the component.
Valid values are
GridBagConstraints.CENTER(the default),GridBagConstraints.NORTH,GridBagConstraints.NORTHEAST,GridBagConstraints.EAST,GridBagConstraints.SOUTHEAST,GridBagConstraints.SOUTH,GridBagConstraints.SOUTHWEST,GridBagConstraints.WEST, andGridBagConstraints.NORTHWEST. GridBagConstraints.weightx,GridBagConstraints.weighty- Used to determine how to distribute space, which is
important for specifying resizing behavior.
Unless you specify a weight for at least one component
in a row (
weightx) and column (weighty), all the components clump together in the center of their container. This is because when the weight is zero (the default), theGridBagLayoutobject puts any extra space between its grid of cells and the edges of the container.
The following figure shows ten components (all buttons) managed by a grid bag layout:
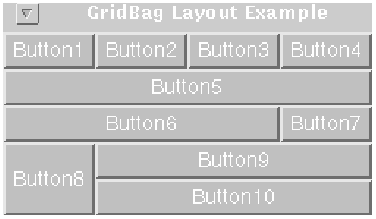
Each of the ten components has the fill field
of its associated GridBagConstraints object
set to GridBagConstraints.BOTH.
In addition, the components have the following non-default constraints:
- Button1, Button2, Button3:
weightx = 1.0 - Button4:
weightx = 1.0,gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER - Button5:
gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER - Button6:
gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.RELATIVE - Button7:
gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER - Button8:
gridheight = 2,weighty = 1.0 - Button9, Button 10:
gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER
Here is the code that implements the example shown above:
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
public class GridBagEx1 extends Applet {
protected void makebutton(String name,
GridBagLayout gridbag,
GridBagConstraints c) {
Button button = new Button(name);
gridbag.setConstraints(button, c);
add(button);
}
public void init() {
GridBagLayout gridbag = new GridBagLayout();
GridBagConstraints c = new GridBagConstraints();
setFont(new Font("Helvetica", Font.PLAIN, 14));
setLayout(gridbag);
c.fill = GridBagConstraints.BOTH;
c.weightx = 1.0;
makebutton("Button1", gridbag, c);
makebutton("Button2", gridbag, c);
makebutton("Button3", gridbag, c);
c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //end row
makebutton("Button4", gridbag, c);
c.weightx = 0.0; //reset to the default
makebutton("Button5", gridbag, c); //another row
c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.RELATIVE; //next-to-last in row
makebutton("Button6", gridbag, c);
c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //end row
makebutton("Button7", gridbag, c);
c.gridwidth = 1; //reset to the default
c.gridheight = 2;
c.weighty = 1.0;
makebutton("Button8", gridbag, c);
c.weighty = 0.0; //reset to the default
c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //end row
c.gridheight = 1; //reset to the default
makebutton("Button9", gridbag, c);
makebutton("Button10", gridbag, c);
setSize(300, 100);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Frame f = new Frame("GridBag Layout Example");
GridBagEx1 ex1 = new GridBagEx1();
ex1.init();
f.add("Center", ex1);
f.pack();
f.setSize(f.getPreferredSize());
f.show();
}
}
- Since:
- JDK1.0
- See Also:
GridBagConstraints, Serialized Form
| Field Summary | |
double[] |
columnWeights
This field holds the overrides to the column weights. |
int[] |
columnWidths
This field holds the overrides to the column minimum width. |
protected Hashtable |
comptable
This hashtable maintains the association between a component and its gridbag constraints. |
protected GridBagConstraints |
defaultConstraints
This field holds a gridbag constraints instance containing the default values, so if a component does not have gridbag constraints associated with it, then the component will be assigned a copy of the defaultConstraints. |
protected java.awt.GridBagLayoutInfo |
layoutInfo
This field holds tha layout information for the gridbag. |
protected static int |
MAXGRIDSIZE
The maximum number of grid positions (both horizontally and vertically) that can be laid out by the grid bag layout. |
protected static int |
MINSIZE
The smallest grid that can be laid out by the grid bag layout. |
protected static int |
PREFERREDSIZE
|
int[] |
rowHeights
This field holds the overrides to the row minimum heights. |
double[] |
rowWeights
This field holds the overrides to the row weights. |
| Constructor Summary | |
GridBagLayout()
Creates a grid bag layout manager. |
|
| Method Summary | |
void |
addLayoutComponent(Component comp,
Object constraints)
Adds the specified component to the layout, using the specified constraint object. |
void |
addLayoutComponent(String name,
Component comp)
Adds the specified component with the specified name to the layout. |
protected void |
AdjustForGravity(GridBagConstraints constraints,
Rectangle r)
|
protected void |
ArrangeGrid(Container parent)
|
GridBagConstraints |
getConstraints(Component comp)
Gets the constraints for the specified component. |
float |
getLayoutAlignmentX(Container parent)
Returns the alignment along the x axis. |
float |
getLayoutAlignmentY(Container parent)
Returns the alignment along the y axis. |
int[][] |
getLayoutDimensions()
Determines column widths and row heights for the layout grid. |
protected java.awt.GridBagLayoutInfo |
GetLayoutInfo(Container parent,
int sizeflag)
Print the layout constraints. |
Point |
getLayoutOrigin()
Determines the origin of the layout grid. |
double[][] |
getLayoutWeights()
Determines the weights of the layout grid's columns and rows. |
protected Dimension |
GetMinSize(Container parent,
java.awt.GridBagLayoutInfo info)
|
void |
invalidateLayout(Container target)
Invalidates the layout, indicating that if the layout manager has cached information it should be discarded. |
void |
layoutContainer(Container parent)
Lays out the specified container using this grid bag layout. |
Point |
location(int x,
int y)
Determines which cell in the layout grid contains the point specified by (x, y). |
protected GridBagConstraints |
lookupConstraints(Component comp)
Retrieves the constraints for the specified component. |
Dimension |
maximumLayoutSize(Container target)
Returns the maximum dimensions for this layout given the components in the specified target container. |
Dimension |
minimumLayoutSize(Container parent)
Determines the minimum size of the target container
using this grid bag layout. |
Dimension |
preferredLayoutSize(Container parent)
Determines the preferred size of the target
container using this grid bag layout. |
void |
removeLayoutComponent(Component comp)
Removes the specified component from this layout. |
void |
setConstraints(Component comp,
GridBagConstraints constraints)
Sets the constraints for the specified component in this layout. |
String |
toString()
Returns a string representation of this grid bag layout's values. |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, wait, wait, wait |
| Field Detail |
MAXGRIDSIZE
protected static final int MAXGRIDSIZE
- The maximum number of grid positions (both horizontally and vertically) that can be laid out by the grid bag layout.
MINSIZE
protected static final int MINSIZE
- The smallest grid that can be laid out by the grid bag layout.
PREFERREDSIZE
protected static final int PREFERREDSIZE
comptable
protected Hashtable comptable
- This hashtable maintains the association between
a component and its gridbag constraints.
The Keys in comptable are the components and the
values are the instances of GridBagConstraints.
- See Also:
GridBagConstraints
defaultConstraints
protected GridBagConstraints defaultConstraints
- This field holds a gridbag constraints instance
containing the default values, so if a component
does not have gridbag constraints associated with
it, then the component will be assigned a
copy of the
defaultConstraints.
layoutInfo
protected java.awt.GridBagLayoutInfo layoutInfo
- This field holds tha layout information
for the gridbag. The information in this field
is based on the most recent validation of the
gridbag.
If
layoutInfoisnullthis indicates that there are no components in the gridbag or if there are components, they have not yet been validated.- See Also:
GetLayoutInfo(Container, int)
columnWidths
public int[] columnWidths
- This field holds the overrides to the column minimum
width. If this field is non-null the values are
applied to the gridbag after all of the minimum columns
widths have been calculated.
If columnWidths has more elements than the number of
columns, columns are added to the gridbag to match
the number of elements in columnWidth.
- See Also:
getLayoutDimensions()
rowHeights
public int[] rowHeights
- This field holds the overrides to the row minimum
heights. If this field is non-null the values are
applied to the gridbag after all of the minimum row
heights have been calculated.
If rowHeights has more elements than the number of
rows, rowa are added to the gridbag to match
the number of elements in rowHeights.
- See Also:
getLayoutDimensions()
columnWeights
public double[] columnWeights
- This field holds the overrides to the column weights. If this field is non-null the values are applied to the gridbag after all of the columns weights have been calculated. If columnWeights[i] > weight for column i, then column i is assigned the weight in columnWeights[i]. If columnWeights has more elements than the number of columns, the excess elements are ignored - they do not cause more columns to be created.
rowWeights
public double[] rowWeights
- This field holds the overrides to the row weights. If this field is non-null the values are applied to the gridbag after all of the rows weights have been calculated. If rowWeights[i] > weight for row i, then row i is assigned the weight in rowWeights[i]. If rowWeights has more elements than the number of rows, the excess elements are ignored - they do not cause more rows to be created.
| Constructor Detail |
GridBagLayout
public GridBagLayout()
- Creates a grid bag layout manager.
| Method Detail |
setConstraints
public void setConstraints(Component comp, GridBagConstraints constraints)
- Sets the constraints for the specified component in this layout.
- Parameters:
comp- the component to be modified.constraints- the constraints to be applied.
getConstraints
public GridBagConstraints getConstraints(Component comp)
- Gets the constraints for the specified component. A copy of
the actual
GridBagConstraintsobject is returned.- Parameters:
comp- the component to be queried.- Returns:
- the constraint for the specified component in this grid bag layout; a copy of the actual constraint object is returned.
lookupConstraints
protected GridBagConstraints lookupConstraints(Component comp)
- Retrieves the constraints for the specified component.
The return value is not a copy, but is the actual
GridBagConstraintsobject used by the layout mechanism.- Parameters:
comp- the component to be queried- Returns:
- the contraints for the specified component.
getLayoutOrigin
public Point getLayoutOrigin()
- Determines the origin of the layout grid.
Most applications do not call this method directly.
- Returns:
- the origin of the cell in the top-left corner of the layout grid.
- Since:
- JDK1.1
getLayoutDimensions
public int[][] getLayoutDimensions()
- Determines column widths and row heights for the layout grid.
Most applications do not call this method directly.
- Returns:
- an array of two arrays, containing the widths of the layout columns and the heights of the layout rows.
- Since:
- JDK1.1
getLayoutWeights
public double[][] getLayoutWeights()
- Determines the weights of the layout grid's columns and rows.
Weights are used to calculate how much a given column or row
stretches beyond its preferred size, if the layout has extra
room to fill.
Most applications do not call this method directly.
- Returns:
- an array of two arrays, representing the horizontal weights of the layout columns and the vertical weights of the layout rows.
- Since:
- JDK1.1
location
public Point location(int x, int y)
- Determines which cell in the layout grid contains the point
specified by
(x, y). Each cell is identified by its column index (ranging from 0 to the number of columns minus 1) and its row index (ranging from 0 to the number of rows minus 1).If the
(x, y)point lies outside the grid, the following rules are used. The column index is returned as zero ifxlies to the left of the layout, and as the number of columns ifxlies to the right of the layout. The row index is returned as zero ifylies above the layout, and as the number of rows ifylies below the layout.- Parameters:
x- the x coordinate of a point.y- the y coordinate of a point.- Returns:
- an ordered pair of indexes that indicate which cell in the layout grid contains the point (x, y).
- Since:
- JDK1.1
addLayoutComponent
public void addLayoutComponent(String name, Component comp)
- Adds the specified component with the specified name to the layout.
- Specified by:
addLayoutComponentin interfaceLayoutManager
- Parameters:
name- the name of the component.comp- the component to be added.
addLayoutComponent
public void addLayoutComponent(Component comp, Object constraints)
- Adds the specified component to the layout, using the specified
constraint object.
- Specified by:
addLayoutComponentin interfaceLayoutManager2
- Parameters:
comp- the component to be added.constraints- an object that determines how the component is added to the layout.
removeLayoutComponent
public void removeLayoutComponent(Component comp)
- Removes the specified component from this layout.
Most applications do not call this method directly.
- Specified by:
removeLayoutComponentin interfaceLayoutManager
- Parameters:
comp- the component to be removed.- See Also:
Container.remove(java.awt.Component),Container.removeAll()
preferredLayoutSize
public Dimension preferredLayoutSize(Container parent)
- Determines the preferred size of the
targetcontainer using this grid bag layout.Most applications do not call this method directly.
- Specified by:
preferredLayoutSizein interfaceLayoutManager
- Parameters:
target- the container in which to do the layout.- See Also:
Container.getPreferredSize()
minimumLayoutSize
public Dimension minimumLayoutSize(Container parent)
- Determines the minimum size of the
targetcontainer using this grid bag layout.Most applications do not call this method directly.
- Specified by:
minimumLayoutSizein interfaceLayoutManager
- Parameters:
target- the container in which to do the layout.- See Also:
Container.doLayout()
maximumLayoutSize
public Dimension maximumLayoutSize(Container target)
- Returns the maximum dimensions for this layout given the components
in the specified target container.
- Specified by:
maximumLayoutSizein interfaceLayoutManager2
- Parameters:
target- the component which needs to be laid out- See Also:
Container,minimumLayoutSize(Container),preferredLayoutSize(Container)
getLayoutAlignmentX
public float getLayoutAlignmentX(Container parent)
- Returns the alignment along the x axis. This specifies how
the component would like to be aligned relative to other
components. The value should be a number between 0 and 1
where 0 represents alignment along the origin, 1 is aligned
the furthest away from the origin, 0.5 is centered, etc.
- Specified by:
getLayoutAlignmentXin interfaceLayoutManager2
getLayoutAlignmentY
public float getLayoutAlignmentY(Container parent)
- Returns the alignment along the y axis. This specifies how
the component would like to be aligned relative to other
components. The value should be a number between 0 and 1
where 0 represents alignment along the origin, 1 is aligned
the furthest away from the origin, 0.5 is centered, etc.
- Specified by:
getLayoutAlignmentYin interfaceLayoutManager2
invalidateLayout
public void invalidateLayout(Container target)
- Invalidates the layout, indicating that if the layout manager
has cached information it should be discarded.
- Specified by:
invalidateLayoutin interfaceLayoutManager2
layoutContainer
public void layoutContainer(Container parent)
- Lays out the specified container using this grid bag layout.
This method reshapes components in the specified container in
order to satisfy the contraints of this
GridBagLayoutobject.Most applications do not call this method directly.
- Specified by:
layoutContainerin interfaceLayoutManager
- Parameters:
parent- the container in which to do the layout.- See Also:
Container,Container.doLayout()
toString
public String toString()
- Returns a string representation of this grid bag layout's values.
- Returns:
- a string representation of this grid bag layout.
GetLayoutInfo
protected java.awt.GridBagLayoutInfo GetLayoutInfo(Container parent, int sizeflag)
- Print the layout constraints. Useful for debugging.
AdjustForGravity
protected void AdjustForGravity(GridBagConstraints constraints, Rectangle r)
GetMinSize
protected Dimension GetMinSize(Container parent, java.awt.GridBagLayoutInfo info)
ArrangeGrid
protected void ArrangeGrid(Container parent)
|
JavaTM 2 Platform Std. Ed. v1.3.1 |
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: INNER | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||
Submit a bug or feature
For further API reference and developer documentation, see Java 2 SDK SE Developer Documentation. That documentation contains more detailed, developer-targeted descriptions, with conceptual overviews, definitions of terms, workarounds, and working code examples.
Java, Java 2D, and JDBC are trademarks or registered trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the US and other countries.
Copyright 1993-2001 Sun Microsystems, Inc. 901 San Antonio Road
Palo Alto, California, 94303, U.S.A. All Rights Reserved.
